Laser cutting principle
Laser cutting is an advanced and widely used cutting process in material processing. It is a processing method that uses a high-energy-density laser beam as a "cutting tool" to thermally cut materials. The use of laser cutting technology can realize the cutting of various metals, non-metallic sheets, composite materials, etc., and has a wide range of applications in various fields.
Laser cutting is to irradiate the workpiece with a focused laser beam, so that the material at the irradiated place is rapidly melted, vaporized, ablated or reaches the ignition point. Laser cutting is one of the thermal cutting methods.
.png) The main way of laser cutting
1. Laser melting cutting
The main way of laser cutting
1. Laser melting cutting
Laser melting and cutting is to use laser heating to melt the metal material, and then spray non-oxidizing gas (N2, Air, etc.) through the nozzle coaxial with the beam to remove the liquid metal by the strong pressure of the gas to form a slit. Laser melting cutting is mainly used for cutting materials that are not easily oxidized or active metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum and their alloys.
2. Laser oxygen cutting
The principle of laser oxygen cutting is similar to oxyacetylene cutting. It uses laser as preheating heat source and oxygen and other active gases as cutting gas. On the one hand, the ejected gas interacts with the metal to undergo an oxidation reaction, releasing a large amount of oxidation heat; on the other hand, the molten oxide and melt are blown out from the reaction zone to form a cut in the metal. Laser oxygen cutting is mainly used for easily oxidized metal materials such as carbon steel. It can also be used for processing materials such as stainless steel, but the section is black and rough, and its cost is lower than that of inert gas cutting.
3. Flame cutting
Oxygen cutting is the standard process for cutting mild steel, using oxygen as the cutting gas. Oxygen was pressurized to 6 bar and then blown into the incision. There, the heated metal reacts with oxygen: it begins to burn and oxidize. The chemical reaction releases a large amount of energy (up to 5 times the laser energy) to assist the laser beam cutting.
4. Melt cutting
Fusion cutting is another standard process for cutting metal. Can also be used to cut other fusible materials such as ceramics. Using nitrogen or argon as the cutting gas, blow a gas pressure of 2 to 20 bar through the incision. Argon and nitrogen are both inert gases, which means they don't react with the molten metal inside the cut, just blow them to the bottom. At the same time, the inert gas can protect the cutting edge from being oxidized by air.
5. Compressed air cutting
Compressed air can also be used to cut thin steel sheets. The air pressure of 5-6 bar is enough to blow away the molten metal in the cut. Since nearly 80% of the air is nitrogen, compressed air cutting is basically fusion cutting.
6. Plasma Assisted Cutting
Plasma clouds appear in plasma-assisted cutting cuts if the parameters are chosen properly. The plasma cloud consists of ionized metal vapor and ionized cutting gas. The plasma cloud absorbs the energy of the CO2 laser and converts it into the workpiece, so that more energy is coupled to the workpiece and the material melts faster, enabling faster cutting. Therefore, this cutting process is also called high-speed plasma cutting.
.png) Basic operation steps of laser cutting
Basic operation steps of laser cutting
1. First fix the material to be cut on the work surface of the laser cutting machine.
2. Then adjust the equipment parameters according to the material and thickness of the metal sheet.
3. Then select the appropriate lenses and nozzles, and inspect them before starting the machine to check the integrity and cleanliness of the machine.
4. Then adjust the cutting head to the appropriate focus position according to the cutting thickness and cutting requirements.
5. Select the appropriate cutting gas and check whether the gas ejection state is normal and good.
6. Try to cut the material. After the material is cut, check the verticality, roughness of the cut surface and whether there is burr or slag.
7. Analyze the cutting surface and adjust the cutting parameters accordingly until the process of the sample cutting surface meets the standard.
8. Carry out the programming of the workpiece drawing and the layout of the whole board cutting, and then import the cutting software system.
9. Adjust the cutting head and focus distance, prepare auxiliary gas, and start cutting.
10. Finally, check the process of the sample. If there is any problem, adjust the parameters in time until the cutting meets the requirements of the process.
.png) Precautions for laser cutting
Precautions for laser cutting
1. Comply with the general cutting machine safety operation rules. Start the laser strictly according to the laser start-up procedure.
2. Wear labor protection equipment according to the regulations, and wear protective glasses that meet the regulations near the laser beam.
3. The operator must be trained, familiar with the structure and performance of the equipment, and master the relevant knowledge of the operating system.
4. When the equipment is started, the operator shall not leave the post without authorization or be in charge of the trustee. If it is really necessary to leave, the operator should stop or cut off the power switch.
5. Do not process a material without knowing whether it can be irradiated or heated with a laser, to avoid the potential danger of fumes and vapors.
6. Keep the fire extinguisher within easy reach; turn off the laser or shutter when not processing; do not place paper, cloth or other flammable objects near the unprotected laser beam.
7. When an abnormality is found in the processing process, it should be stopped immediately, and the fault should be eliminated or reported to the supervisor in time.
8. Keep the laser, bed and surrounding sites clean, orderly and free of oil pollution, and stack workpieces, plates and wastes according to regulations.
9. When using gas cylinders, avoid crushing the welding wires to avoid leakage accidents. The use and transportation of gas cylinders shall comply with the gas cylinder monitoring regulations. Do not expose gas cylinders to sunlight or near heat sources. When opening the bottle valve, the operator must stand on the side of the bottle mouth.
10. Observe high-voltage safety regulations during maintenance. Follow regulations and procedures every 40 hours of operation or weekly maintenance, every 1000 hours of operation or every six months.
11. After starting the machine, manually start the machine tool in the X and Y directions at low speed and check to see if there is any abnormality.
12. After inputting the new workpiece program, it should be tested first and check its operation.
13. When working, pay attention to observe the operation of the machine tool to avoid accidents caused by the cutting machine going out of the effective stroke range or the collision of two machines.
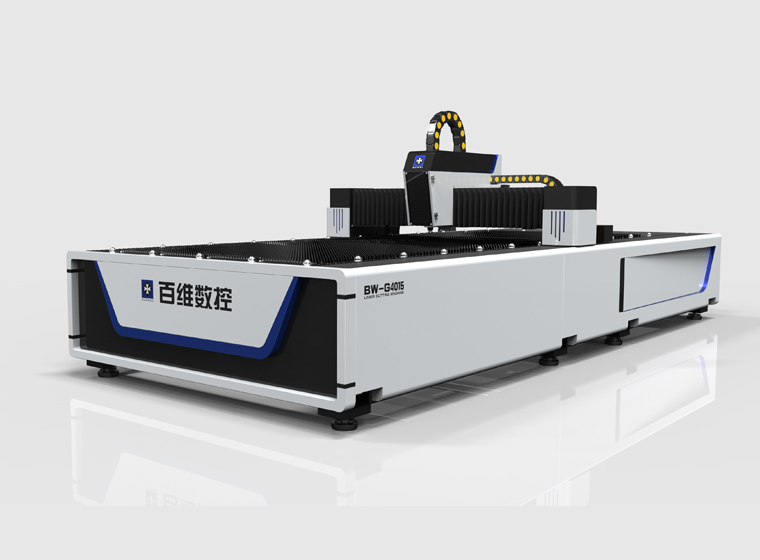 BW-G3015 3kw open type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G3015 3kw open type fiber laser cutting machine BW-G4020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G4020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine BW-G6020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G6020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine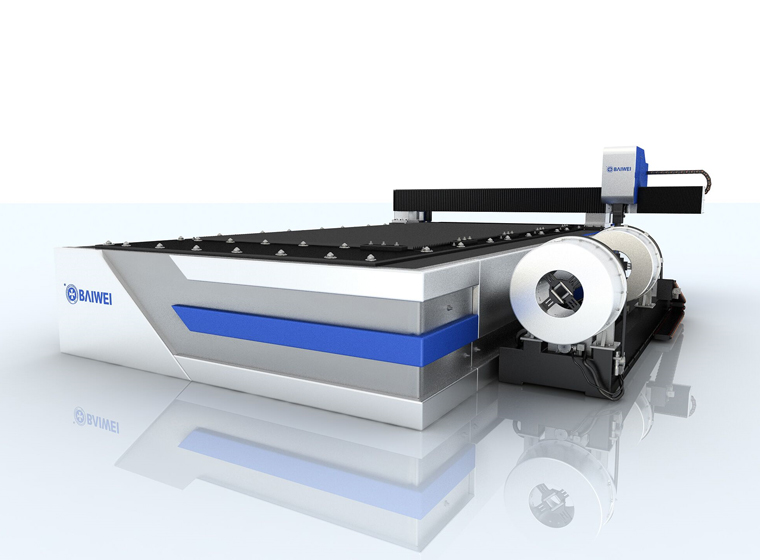 BW3000 6kw open type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine
BW3000 6kw open type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine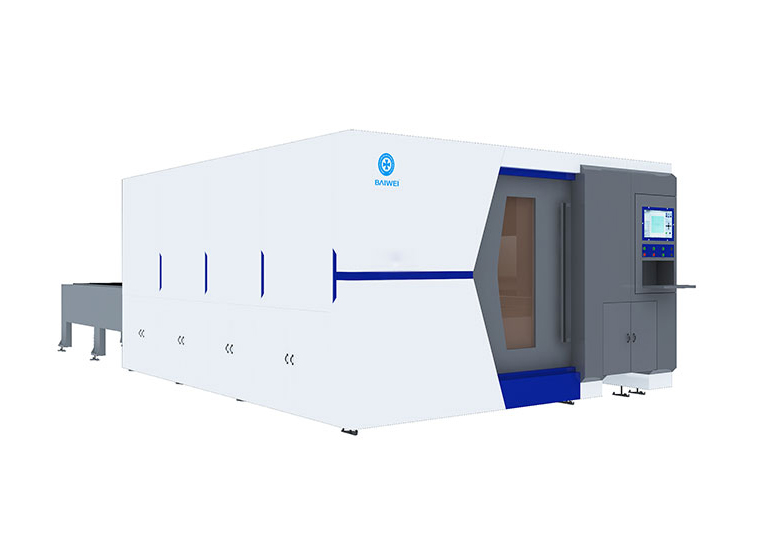 BW3000 6KW closed type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine
BW3000 6KW closed type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine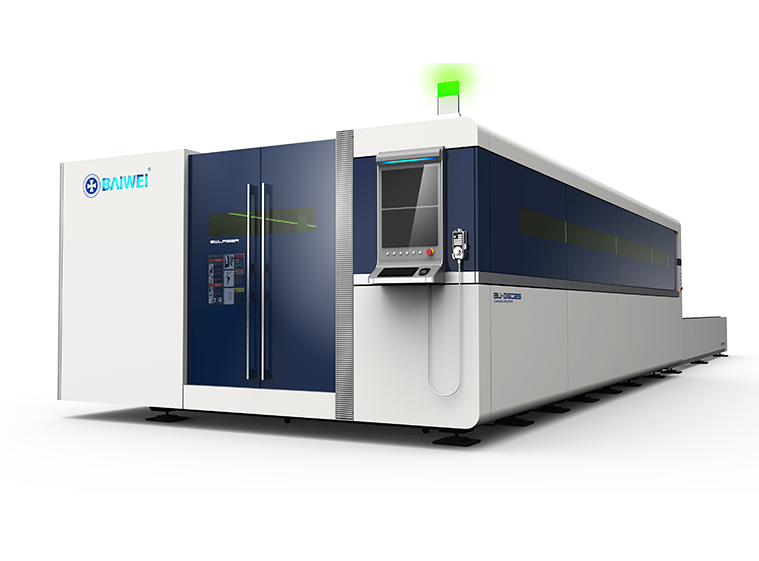 BW-G6025 Closed type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G6025 Closed type fiber laser cutting machine BW-G12025 Closed type metal sheet laser cutting machine machine
BW-G12025 Closed type metal sheet laser cutting machine machine.jpg) BWQG SERIES Professional Laser Tube Cutting Machine 3kw-20kw
BWQG SERIES Professional Laser Tube Cutting Machine 3kw-20kw
.jpg)



.jpg)


.png)
.png)
.png)
