1.Laser vaporization cutting
Using a high-energy-density laser beam to heat the workpiece, the temperature rises rapidly, reaching the boiling point of the material in a very short time. , the material begins to evaporate, forming a vapor. These steams are ejected at high speed, and while the steam is ejected, cuts are formed in the material. The vaporization heat of the material is generally large, so the laser vaporization cutting requires a large power and power density.Laser vaporization cutting is mostly used for the cutting of extremely thin metal materials and non-metal materials (such as paper, cloth, wood, plastic and rubber, etc.).
 2.Laser fusing beam laser
2.Laser fusing beam laser
When laser fusing, the metal material is melted by laser heating, and then non-oxidizing gas (Ar, He, N, etc.) is sprayed through the coaxial nozzle. The beam relies on the strong pressure of the gas to push the liquid metal out, forming the incision. Laser melting cutting does not need to completely vaporize the metal, and the energy required is only 1/10 of the vaporized cutting.
Laser melting cutting is mainly used to cut some materials that are not easily oxidized or active metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum and their alloys.
 3.Laser Oxygen Cutting
3.Laser Oxygen Cutting
The principle of laser oxygen cutting is similar to oxyacetylene cutting. It uses a laser as a preheating heat source and a reactive gas such as oxygen as a cutting gas. On the one hand, the blown gas reacts with the cutting metal, releasing a large amount of oxidation heat; on the other hand, molten oxide and melt are blown out from the reaction zone, forming a cut in the metal. Since the oxidation reaction in the cutting process generates a lot of heat, the energy required for laser oxygen cutting is only 1/2 of that of melting cutting, and the cutting speed is much higher than that of laser steam cutting and melting cutting.
Laser oxygen cutting is mainly used for carbon steel, titanium steel, heat-treated steel and other easily oxidized metal materials.
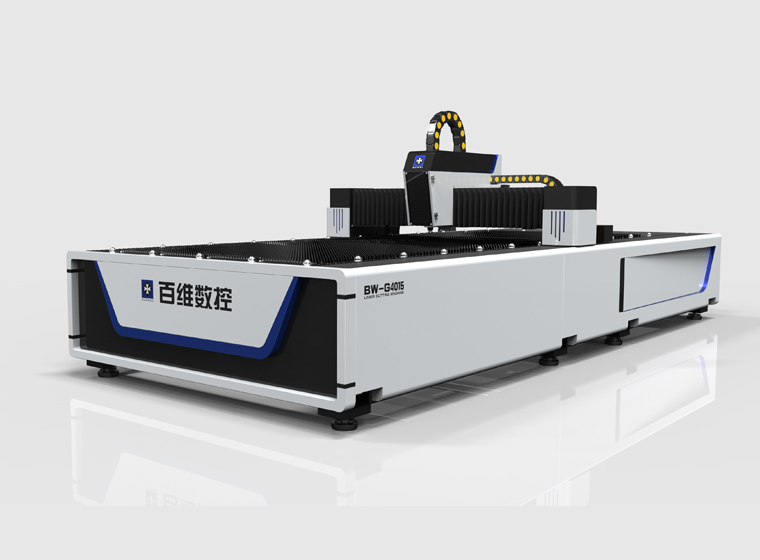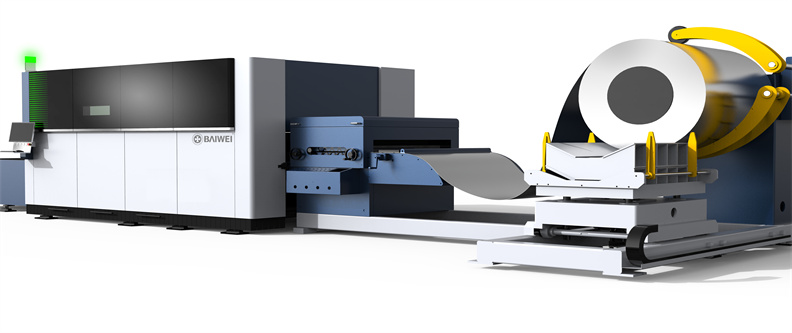
 BW-G3015 3kw open type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G3015 3kw open type fiber laser cutting machine BW-G4020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G4020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine BW-G6020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G6020 Open type fiber laser cutting machine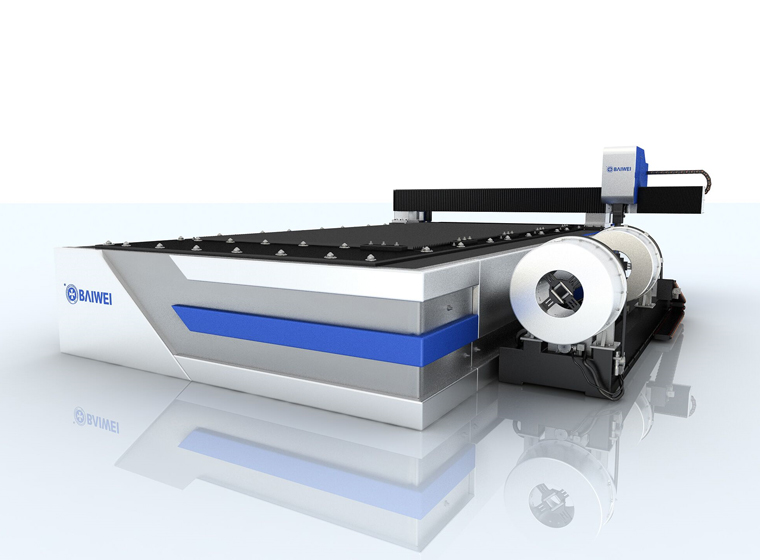 BW3000 6kw open type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine
BW3000 6kw open type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine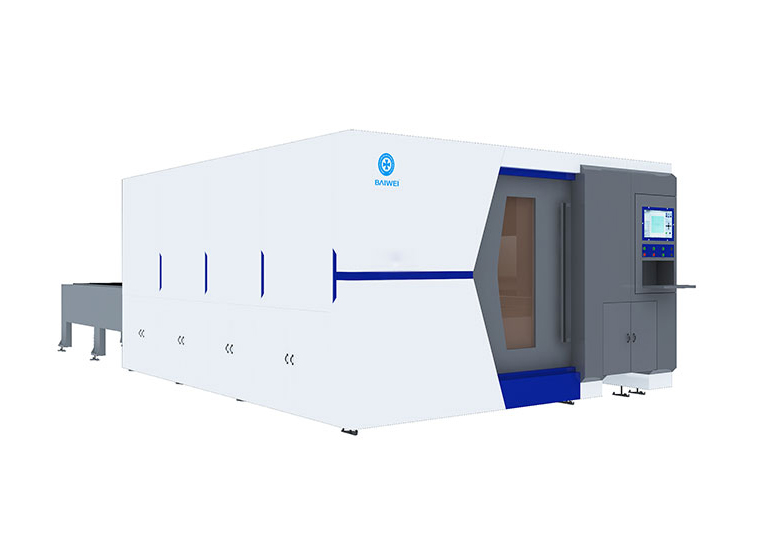 BW3000 6KW closed type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine
BW3000 6KW closed type fiber laser plate&tube cutting machine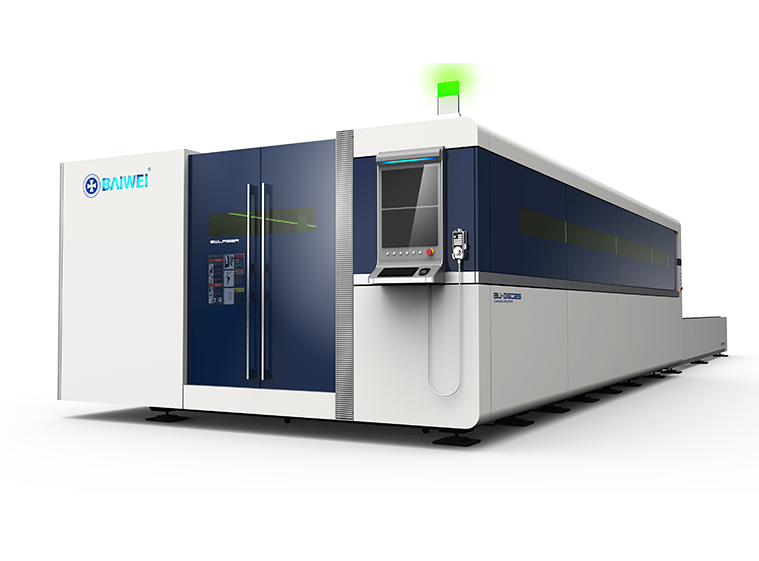 BW-G6025 Closed type fiber laser cutting machine
BW-G6025 Closed type fiber laser cutting machine BW-G12025 Closed type metal sheet laser cutting machine machine
BW-G12025 Closed type metal sheet laser cutting machine machine.jpg) BWQG SERIES Professional Laser Tube Cutting Machine 3kw-20kw
BWQG SERIES Professional Laser Tube Cutting Machine 3kw-20kw
.jpg)



.jpg)





